59 Pr (Praseodymium)
It is a soft, malleable, silvery and ductile.
It react slowly with oxygen, and It develop a green oxide coating that falls off when exposed to air.
So it should be stored in light mineral oil or in sealed in plastic material to prevent from contact with air.
But it is more resistant to corrosion in air than the other rare metals.

Identity
CAS Number: CAS7440-10-0
CID Number: CID23942
CONTENT INDEX
Basic Properties of Praseodymium
Pronunciation: Pray-zee-o-dim-ee-am
Appearance: Grayish white
Mass Number: 141
Standard Atomic weight: 140.908 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 59
Electrons: 59
Protons: 59
Neutrons: 82
Period: 6
Block: f
Element category: Lanthanide
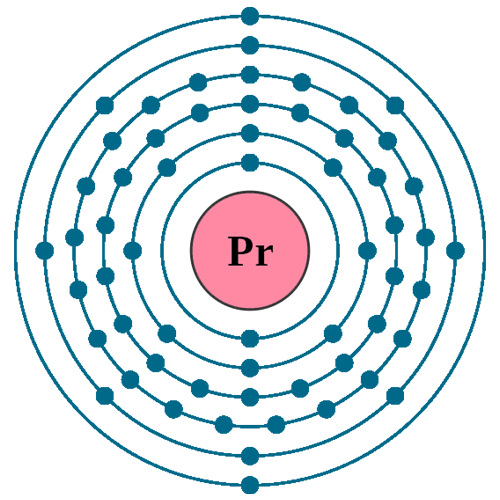
Electrons per shell: K2, L8, M18, N21, O8, P2
Electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p64f36s2
Thermal Properties of Praseodymium
Phase: Solid
Melting point: 1208 K (935 oC, 1715 oF)
Boiling point: 3403 K (3130 oC, 5666 oF)
Fusion heat: 6.89 kJ/mol
Vaporization heat: 331 kJ/mol
Molar heat capacity: 27.20 J/(mol.K)
Thermal expansion: α, poly: 6.7 μm/(m∙K)
Thermal conductivity: 12.5 W/(m∙K)
Electrical properties of Praseodymium
Electrical conductivity: 1.4×106 S/m
A Electrical resistivity: α, poly: 0.700 μΩ∙m
A Electrical type: Conductor
Magnetic Properties of Praseodymium
A Magnetic type: Paramagnetic
Magnetic susceptibility (xmol): +5010×10-6 cm3/mol
Volume magnetic susceptibility: 0.0028087
Mass magnetic susceptibility: 423×10-9 m3/kg
Molar magnetic susceptibility: 59.604×10-9 m3/mol
Physical Properties of Praseodymium
Density: 6.77 g/cm3 (In solid) 6.50 g/cm3 (In Liquid)
Molar volume: 0.00002122 m3/mol
Young’s modulus: α form: 37.3 GPa
Shear modulus: α form: 14.8 GPa
Mohs Hardness: 1.41
Bulk modulus: α form: 28.8 GPa
Poisson ratio: α form: 0.281
Vicker hardness: 250-745 MPa
Brinell hardness: 250-640 MPa
Sound Speed: 2280 m/s
Atomic Properties of Praseodymium
Oxidation states: 5,4,3,2,
Valence Electrons: 4f3 6s2
Ion charge: Pr3+
Ionization energies: 1st: 527 kJ.mol 2nd: 1020 kJ/mol 3rd: 2086 kJ/mol
Ionic radius: 103.3 pm
Atomic radius: 239 pm (Van der Waals)
Covalent radius: 203±7 pm
Filling Orbital: 4f3
Crystal structure: Double hexagonal close-packed (At room temperature), Change to Face-centered cubic (At 560 oC), Body-centered cubic (Appear shortly before the melting point of 935 oC)
Grid parameters: a=3.673 Å c=11.84 Å
Attitude c/a: 3.22
Space Group Name: R_3m
Space Group Number: 166
Reactivity of Praseodymium
Electronegativity: pauling scale: 1.13
Valence: +3
Electron affinity: 50 kJ/mol
Nuclear Properties of Praseodymium
Half Life: Stable (Infinity)
Lifetime: Stable (Infinity)
Quantum Number: 4I9/2
Neutron cross section (Brans): 11.4
Neutron Mass Absorption: 0.0029
Isotopes: 141Pr 142Pr 143Pr
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Atomic Mass g/mol | Half Life (t1/2) |
| 141Pr | 100 | 149.908 | Stable |
| 142Pr | Syn | – | 19.12 h |
| 143Pr | Syn | – | 13.57 d |
Chemical Reactions
Praseodymium burns readily at 150 oC to form Praseodymium (lll, lV) oxide:
12 Pr + 11 O2 → 2 Pr6O11
Reacts slowly with cold water and rapidly with hot water:
2 Pr (s) + 6 H2O (l) → 2 Pr(OH)3 (aq) + 3 H2 (g)
The metal reacts with all Halogens to form Trihalides:
2 Pr (s) + 3 F2 (g) → 2 PrF3 (s) [green]
2 Pr (s) + 3 Cl2 (g) → 2 PrCl3 (s) [green]
2 Pr (s) + 3 Br2 (g) → 2 PrBr3 (s) [green]
2 Pr (s) + 3 I2 (g) → 2 PrI3 (s)
Dissolves readily in dilute sulfuric acid:
2 Pr (s) + 3 H2SO4 (aq) → 2 Pr3+ (aq) + 3 SO42−(aq) + 3 H2 (g)
Praseodymium History
Discovery: Carl Auer von Welsbach (1885)
Naming Origin: Greek: prasios (green) and didymos (twin); from its green salts.
Praseodymium Uses
Mischmetal Is an alloy (Containing 50% cerium, 25% lanthanum, Small amounts of Neodymium and Praseodymium), which is used in making cigarette lighter flints.
Praseodymium can be used as alloying agent with magnesium to make high-strength metal, which is used in Aircraft engines.
It is also used in alloys for permanent magnets.
APraseodymium oxide (Pr2O3) is the most refractory substance, Along with other lanthanide elements, It is widely used as a core material for carbon arc lights, which is used by the motion picture industry for studio lighting and projection.
Praseodymium’s salts are used to color glasses and enamels.
Didymium glass (a mixture of Neodymium and Praseodymium) is used as a coloring glass to make welders goggles, which is able to absorb the yellow sodium glare of the flame and infrared (heat) radiation. This kind of glass is used to protect the eyes of welders.
Biological role: It has Low-toxicity, But it should be handled with care.
Abundance of Praseodymium
Samarium is chiefly Found in the minerals monazite and bastnaesite.
It commercially extracted by ion exchange and solvent extraction techniques.
The metal is prepared by reducing anhydrous chloride with calcium.
Annual world wide production is around 2400 tons.
2×10-7% (In Universe)
9.9×10-6% (In Meteorites)
1×10-7% (In Sun)
0.00086% (In Earth’s Crust)
6×10-11% (In Oceans)
World’s Top 3 producers of Praseodymium
1) China
2) Russia
3) Malaysia
World’s Top 3 Reserve holders of Praseodymium
1) China
2) CIS Countries (inc. Russia)
3) USA
#Praseodymium



Thanks, it’s very informative