68 Er (Erbium)

Erbium is a lustrous, silvery metal, soft, malleable.
It is very stable in air, but it reacts very slowly with oxygen and water and dissolves in acids.
It’s Salts are Pink coloured and has a sharp adsorption spectra in visible, ultraviolet and infrared light.

Identity
CAS Number: CAS7440-52-0
CID Number: CID23980
CONTENT INDEX
Basic Properties of Erbium
Pronunciation: Ur-bee-am
Appearance: Silvery white
Mass Number: 167
Standard Atomic weight: 167.259 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 68
Electrons: 68
Protons: 68
Neutrons: 99
Period: 6
Block: f
Element category: Lanthanide
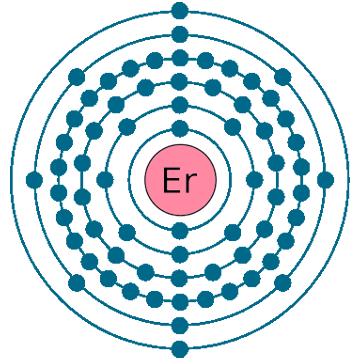
Electrons per shell: K2, L8, M18, N30, O8, P2
Electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p64f126s2
Thermal Properties of Erbium
Phase: Solid
Melting point: 1802 K (1529 oC, 2784 oF)
Boiling point: 3141 K (2868 oC, 5194 oF)
Fusion heat: 19.90 kJ/mol
Vaporization heat: 280 kJ/mol
Molar heat capacity: 28.12 J/(mol.K)
Thermal expansion: poly: 12.2 μm/(m∙K)
Thermal conductivity: 14.5 W/(m∙K)
Neel Point: 82 K
Electrical properties of Erbium
Electrical conductivity: 1.2 x106 S/m
sElectrical resistivity: poly: 0.860 μΩ∙m
sElectrical type: Conductor
Curie point: 32 K
Magnetic Properties of Erbium
sMagnetic type: Paramagnetic
Magnetic susceptibility (xmol): +44,300×10-6 cm3/mol
Volume magnetic susceptibility: 0.0341788
Mass magnetic susceptibility: 3770×10-9 m3/kg
Molar magnetic susceptibility: 630.566×10-9 m3/mol
Physical Properties of Erbium
Density: 9.066 g/cm3 (In solid) 8.86 g/cm3 (In Liquid)
Molar volume: 0.00001845 m3/mol
Young’s modulus: 69.9 GPa
Shear modulus: 28.3 GPa
Mohs Hardness: 1.97
Bulk modulus: 44.4 GPa
Poisson ratio: 0.237
Vicker hardness: 430-700 MPa
Brinell hardness: 600-1070 MPa
Sound Speed: 2830 m/s
Atomic Properties of Erbium
Oxidation states: 3, 2, 1
Valence Electrons: 4f12 6s2
Ion charge: Er3+
Ionization energies: 1st: 589.3 kJ.mol 2nd: 1150 kJ/mol 3rd: 2194 kJ/mol
Ionic radius: 88.1 pm
Atomic radius: 235 pm (Van der Waals)
Covalent radius: 189±6 pm
Filling Orbital: 4f12
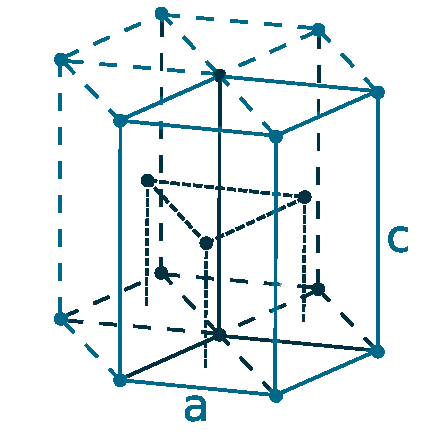
Crystal structure: Hexagonal close-packed
Lattice angles: π/2, π/2, π/3
Lattice constant: 355.88, 355.88, 558.74 pm
Grid parameters: a=3.558 Å, c=5.587 Å
Attitude (c/a): 1.570
Space Group Name: P63/mmc
Space Group Number: 194
Reactivity of Erbium
Electronegativity: pauling scale: 1.24
Valence: 3
Electron affinity: 50 kJ/mol
Nuclear Properties of Erbium
Half Life: Stable (Infinity)
Lifetime: Stable (Infinity)
Quantum Number: 3H6
Neutron cross section (Brans): 165
Neutron Mass Absorption: 0.036
Isotopes: 160Er 162Er 164Er 165Er 166Er 167Er 168Er 169Er 170Er 171Er
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Atomic Mass g/mol | Half Life (t1/2) |
| 160Er | Syn | – | 28.58 h |
| 162Er | 0.139 | 161.928 | Stable |
| 164Er | 1.601 | 163.928 | Stable |
| 165Er | Syn | – | 10.36 h |
| 166Er | 33.503 | 165.930 | Stable |
| 167Er | 22.869 | 166.933 | Stable |
| 168Er | 26.978 | 167.933 | Stable |
| 169Er | Syn | – | 9.4 d |
| 170Er | 14.91 | 169.934 | Stable |
| 171Er | Syn | – | 7.516 h |
| 172Er | Syn | – | 49.3 h |
Chemical Reactions
The metal tarnishes slowly in air and burns readily to form erbium (lll) oxide:
4 Er + 3 O2 → 2 Er2O3
Reacts slowly with cold water and rapidly with hot water (form erbium hydroxide and hydrogen gas):
2 Er (s) + 6 H2O (l) → 2 Er(OH)3 (aq) + 3 H2 (g)
The metal reacts with all Halogens to form Erbium (lll) halides:
2 Er (s) + 3 F2 (g) → 2 ErF3 (s) [pink] (Erbium (lll) fluoride)
2 Er (s) + 3 Cl2 (g) → 2 ErCl3 (s) [violet] (Erbium (lll) chloride)
2 Er (s) + 3 Br2 (g) → 2 ErBr3 (s) [violet] (Erbium (lll) bromide)
2 Er (s) + 3 I2 (g) → 2 ErI3 (s) [violet] (Erbium (lll) iodide)
Dissolves readily in dilute sulfuric acid to form Solutions containing Erbium (lll) ions (Rose red):
2 Er (s) + 3 H2SO4 (aq) → 2 Er3+ (aq) + 3 SO42− (aq) + 3 H2 (g)
Erbium History
Naming: After Ytterby (Sweden), Where it was mined
Discovery: Carl Gustaf Mosander (1843)
Erbium Uses
Erbium has nuclear and metallurgical uses.
When Erbiums alloyed with metals such as vanadium, it lowers their hardness and improves their workability.
Erbium oxide is used to make infrared-absorbing glass (safety glasses for welders and metal workers).
Due to its pink coloured, Erbium is also used to give colour to some sunglasses and imitation gems.
Erbium is used as a photographic filter as well, and to dope optical fibers at regular intervals to amplify signals.
Biological role: It is Low-toxic, it should be handled with care.
Abundance of Erbium
It is found in most important ores are Monazite and bastanite like other rare elements.
It can be extracted by ion exchange and solvent extraction.
Other sources are xenotime and euxenite.
Around 500 tons are produced world wide annually.
2×10-7% (In Universe)
1.8×10-5% (In Meteorites)
1×10-7% (In Sun)
0.0003% (In Earth’s Crust)
9×10-11% (In Oceans)
World’s Top 3 producers of Erbium
1) China
2) Russia
3) Malaysia
World’s Top 3 Reserve holders of Erbium
1) China
2) CIS Countries (inc. Russia)
3) USA
#erbium


