54 Xe (Xenon)

It is a rare, colourless, tasteless and chemically unreactive gas.
A Xenon In a vaccume tube (gas filled tube), produce blue glow light when excited by electrical discharge.
A Xenon is available in sealed glass containers of gas at standard pressure.


Identity
CAS Number: CAS7440-6-3
CID Number: CID23991
DOT Hazard Class: 2.2
DOT Number: 2591
RTECS Number: RTECSZE1280000
CONTENT INDEX
Basic Properties of Xenon
Pronunciation: Zee-non
Appearance: Colourless gas
Mass Number: 131
Standard Atomic weight: 131.293 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 54
Electrons: 54
Protons: 54
Neutrons: 77
Group: 18
Period: 5
Block: p
Element category: Noble gases
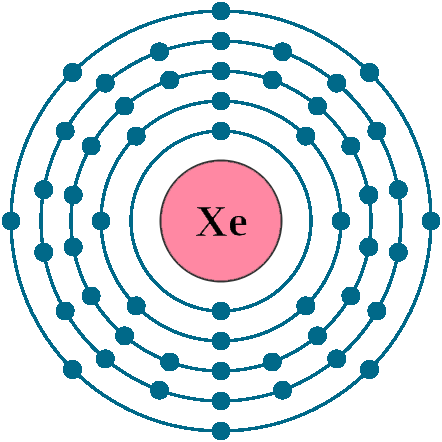
Electrons per shell: K2, L8, M18, N18, O8
Electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p6
Thermal Properties of Xenon
Phase: Gas (monoatomic)
Melting point: 161.40 K (-111.75 oC, -169.15 oF)
Boiling point: 165.051 K (-108.099 oC, -162.578 oF)
Triple Point Temperature: 161.405 K (-111.745 oC, -169.141 oF)
Triple point Pressure: 81.77 kPa (0.807 Atm)
Critical Temperature: 289.733 K (16.583 oC, 61.8494 oF)
Critical Pressure: 5.842 MPa (57.65 Atm)
Fusion heat: 2.27 kJ/mol
Vaporization heat: 12.64 kJ/mol
Specific Heat: 158.32 J/(kg K)
Adiabatic Index: 5/3
Molar heat capacity: 21.01 J/(mol.K)
Thermal conductivity: 5.65×10-3 W/(m∙K)
Magnetic Properties of Xenon
A Magnetic type: Diamagnetic
Magnetic susceptibility (xmol): -43.9×10-6 cm3/mol
Volume magnetic susceptibility: -0.254×10-9
Mass magnetic susceptibility: -4.3×10-9 m3/kg
Molar magnetic susceptibility: -0.565×10-9 m3/mol
Physical Properties of Xenon
Density: 5.894 g/L (In Gas) 2.942 g/cm3 (In Liquid At B.P)
Molar volume: 0.022 m3/mol
Refractive index: 1.000702
Sound Speed: 178 m/s (In Gas), 1090 m/s (In Liquid)
Atomic Properties of Xenon
Oxidation states: 0, +1, +2, +4, +6, +8 (rarely more than 0)
Valence Electrons: 5s2 5p2
Ionization potential of an atom: 12.08
Ionization energies: 1st: 1170.4 kJ.mol 2nd: 2046.4 kJ/mol 3rd: 3099.4 kJ/mol
Atomic radius: 216 pm (Van der Waals)
Covalent radius: 140±9 pm
Filling Orbital: 5p6
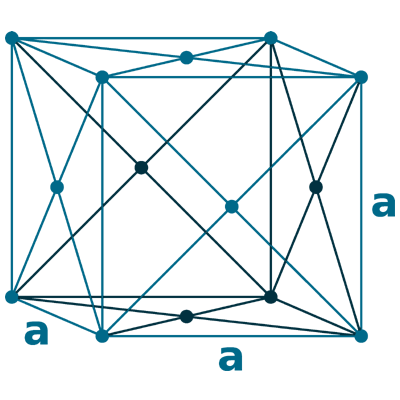
Crystal structure: Face-centered cubic
Lattice angles: π/2, π/2, π/2
Lattice constant: 620.23, 620.23, 620.23 pm
Grid parameters: 6.200 Å
Space Group Name: Fm_3m
Space Group Number: 225
Reactivity of Xenon
Electronegativity: pauling scale: 2.6
Valence: +6
Electron affinity: 0 kJ/mol
Nuclear Properties of Xenon
Half Life: Stable (Infinity)
Lifetime: Stable (Infinity)
Quantum Number: 1S0
Neutron cross section (Brans): 25
Neutron Mass Absorption: 0.0083
Isotopes: 124Xe 125Xe 126Xe 127Xe 128Xe 129Xe 130Xe 131Xe 132Xe 133Xe 134Xe 135Xe 136Xe
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Atomic Mass g/mol | Half Life (t1/2) |
| 124Xe | 0.095 | 123.906 | Stable |
| 125Xe | Syn | – | 16.9 h |
| 126Xe | 0.089 | 125.904 | Stable |
| 127Xe | Syn | – | 36.345 d |
| 128Xe | 1.910 | 127.904 | Stable |
| 129Xe | 26.401 | 128.905 | Stable |
| 130Xe | 4.071 | 129.904 | Stable |
| 131Xe | 21.232 | 130.905 | Stable |
| 132Xe | 26.909 | 131.904 | Stable |
| 133Xe | Syn | – | 5.247 d |
| 134Xe | 10.436 | -133.905 | Stable |
| 135Xe | Syn | – | 9.14 h |
| 136Xe | 8.857 | 135.907 | 2.165×1021 y |
Xenon History
Naming: Greek: xenos (stranger)
Discovery: William Ramsay and Morris Travers (At University College London)
First isolation: Travers (1898)
Xenon Uses
Xenon is used in electron tubes, photographic flash lamps, stroboscopic lamps and bactericidal lamps used in food preparation and processing, High-pressure arc lamps to product UV light (solar simulators) and high-intensity arc-lamps (Projection lamps) for motion picture projection.
It is also used in lamps used to excite ruby lasers that generate coherent light.
Other uses are as a Xenon ‘blue’ fog lights and head lights in some vehicles.
Used in Medical as a General anesthetic or General anesthesia (A machine that can deliver xenon), in Sports Doping (Xenon inhalaled athletes has been failed in sports Doping test) and Neuroprotectant.
It is used in the nuclear energy studies(atomic energy field) in bubble chambers, probes, and other applications where a high molecular weight and inert chemistry is desirable.
The perxenates (Salts of the yellow xenon-containing anion XeO64-) are used in analytical chemistry as oxidizing agents.
Xenon ion propulsion system (XIPS) are used by several satellites to keep them in orbit, and in some other spacecraft, Because it is easily ionized and generating a desirable level of thrust when ions are accelerated.
Xenon difluoride (XeF2) is used to etch silicon microprocessors.
It is also used in the manufacture of 5-fluorouracil (C4H3FN2O2), a drug used to treat certain types of cancer.
Biological role: It is not toxic, but its compounds are highly toxic and explosive because they are strong oxidizing agents.
Abundance of Xenon
Xenon is present in the atmosphere, with only 0.086 parts per million by volume.
It can also be found in some gases that created through mineral springs.
It is Obtain in small quantities by separation from liquified air (Air cooled to very low temperatures, So It condensed into pale blue liquid),
133Xe and 135Xe are radioactive Isotopes that created through neutron irradiation of fissionable material in nuclear reactors.
More than 80 xenon compounds have been made with xenon chemically bonded to fluorine and oxygen.
Annual world wide production is around 0.6 tons.
1×10-6% (In Universe)
2×10-9% (In Earth’s Crust)
5×10-10% (In Oceans)
#xenon



Fantastic post however , I was wondering if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Appreciate it!
Sure..Please Subscribe your email for getting all new updates