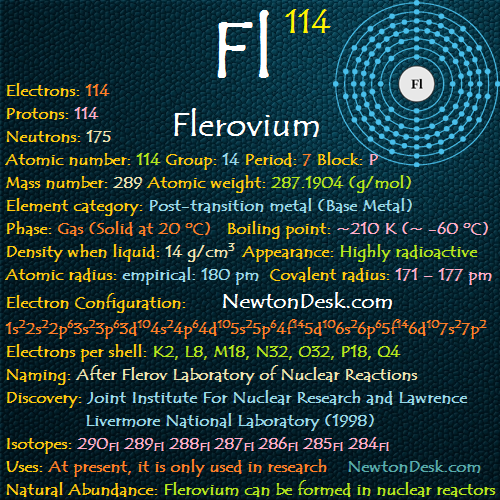
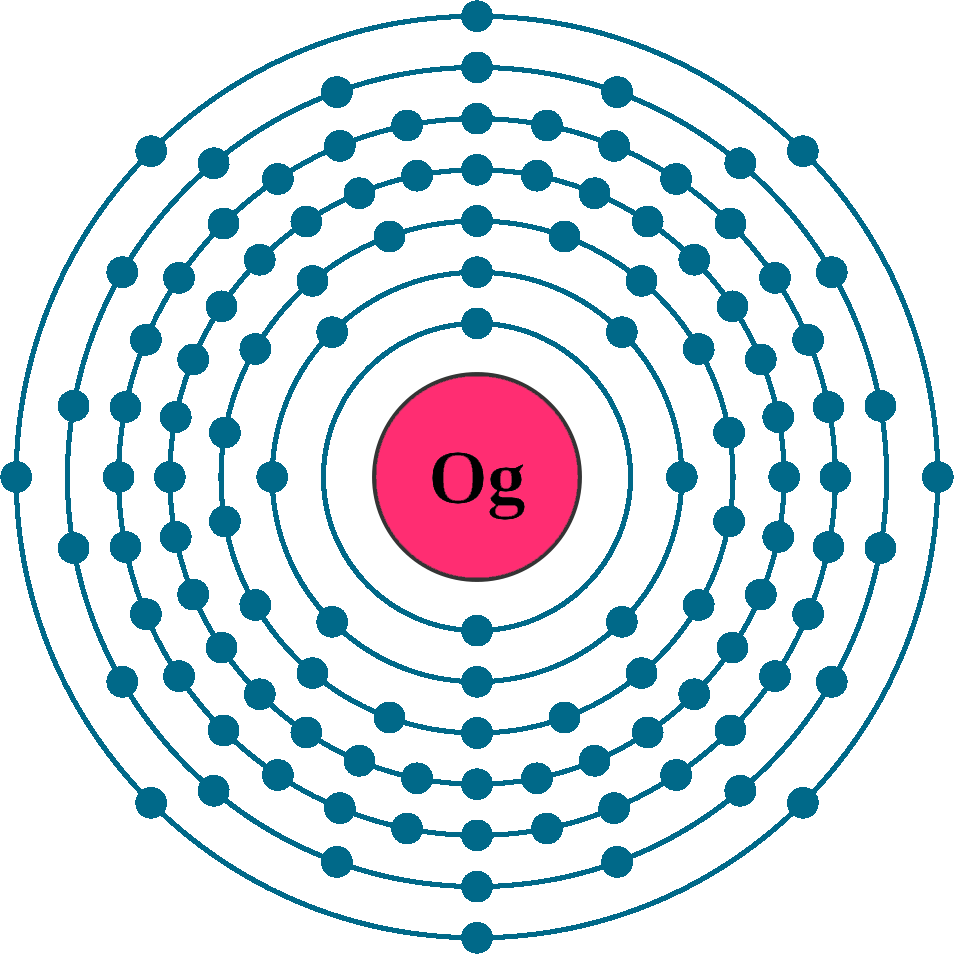
118 Og (Oganesson Element)

CONTENT INDEX
About Oganesson Element
Oganesson is a radioactive and artificially produced element of which little is known. it was expected to be a noble gas but now predicted to be reactive solid and either semiconductor or post-transition metal.
Identity
CAS Number: CAS54144-19-3
CID Number: N/A
DOT Hazard Class: N/A
DOT Number: N/A
RTECS Number: N/A
Properties of Oganesson Element
Basic Properties of Oganesson Element
Pronunciation: Oh-ga-nes-on / Og-a-nes-on
Appearance: N/A
Mass Number: 294 (stable Isotope) (unconfirmed: 295)
Standard Atomic weight: 294.213 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 118
Electrons: 118
Protons: 118
Neutrons: 176
Period: 7
Group: 18
Block: P
Element category: Unkown chemical properties (it was expected to be a noble gas, but now predicted to be reactive solid and either semiconductor or post-transition metal)
Electrons per shell: K1, L8, M18, N32, O32, P18, Q8
Electron configuration: 1s12s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p64f145d106s26p65f146d107s27p6
Thermal Properties of Oganesson
Phase: Solid (predicted)
Melting point: 320 K (50 oC, 120 oF)
Boiling point: 350±30 K (80±30 oC, 170±50 oF)
Debye temperature: N/A
Triple Point Temperature: N/A
Triple Point Pressure: N/A
Critical point Temperature: 439 K (165.85 oC, 330.53 oF)
Critical Point Pressure: 6.8 MPa (67.11 Atm)
Fusion heat: 23.5 kJ/mol (H2)
Vaporization heat: 19.4 kJ/mol
Specific heat: N/A
Molar heat capacity: N/A
Thermal expansion: N/A
Thermal conductivity: N/A
Neel Point (magnetic ordering temperature) TN: N/A
Electrical properties of Oganesson
Electrical conductivity: N/A
Electrical resistivity: N/A
Electrical type: N/A
Critical point (Superconducting point): N/A
Magnetic Properties of Oganesson
Magnetic type: N/A
Curie point: N/A
Magnetic susceptibility (xmol): N/A
Volume magnetic susceptibility: N/A
Mass magnetic susceptibility: N/A
Molar magnetic susceptibility: N/A
Physical Properties of Oganesson
Density: 4.9-5.1 g/cm3 (predicted)
Molar volume: N/A
Young’s modulus: N/A
Shear modulus: N/A
Mohs Hardness: N/A
Bulk modulus: N/A
Poisson ratio: N/A
Vicker hardness: N/A
Brinell hardness: N/A
Refractive Index: N/A
Sound Speed: N/A
Atomic Properties of Oganesson
Oxidation states: -1, 0, +1, +2, +4, +6 (predicted)
Valence Electrons: N/A
Ion charge: N/A
The ionization potential of an atom: N/A
Ionization energies: 1st: 860 kJ/mol 2nd: 1560 kJ/mol (predicted)
Ionic radius: N/A
Atomic radius: 152 pm
Van der Waals: N/A
Covalent radius: 157 pm (predicted)
Filling Orbital: N/A
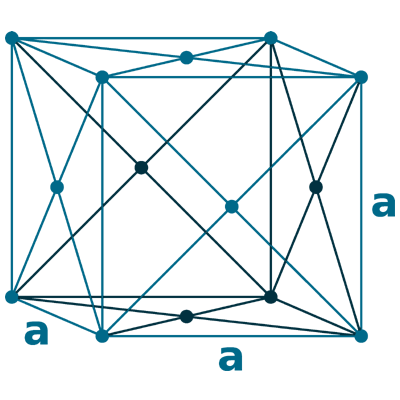
Crystal structure: Face centered cubic (FCC)
Lattice angles: N/A
Lattice constant: N/A
Grid parameters: N/A
Attitude c/a: N/A
Space Group Name: N/A
Space Group Number: N/A
Reactivity of Oganesson
Electronegativity: N/A
Valence: N/A
Electron affinity: N/A
Nuclear Properties of Oganesson Element
Half Life: 5 ms
Lifetime: 7 ms
Decay Mode: Alpha Emission
Quantum Number: 1S0
Neutron cross section (Brans): N/A
Neutron Mass Absorption: N/A
Isotopes: 294Og 295Og
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Atomic Mass g/mol | Half Life (t1/2) |
| 294Og | Syn | 294.215 | 0.69 ms |
| 295Og | Syn | – | 181 ms? |
Chemical Reactions of Oganesson
At Presently research is going on.
Oganesson History
Naming: In honour of Yuri Oganessian (Russian nuclear Physicist)
Discover By: Scientists from Joint institute for Nuclear Research (JINR), in Dubna (Russia) and Lawrence Livemore National Laboratory (LLNL), In California (USA) (2002)
Prediction by: Hans Peter Jorgen Julius Thomsen (1895)
Discovery of Oganesson Element
In 1998, Polish physicist Robert Smolańczuk suggested by calculations that it might be possible to make oganesson by fussion Lead with krypton under carefully controlled conditions.
In 1999, at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), The Researchers announced the discovery of Oganesson and Livermorium, where they reported thet they had performed the reaction.
20882Pb + 8636Kr → 293118Og + n.
In 2002, At the Joint Insititute for Nuclear Research (JINR), the first decay of atoms of Oganesson was observed by a joint team of American and Russian scientists, which headed by Yuri Oganessian. But The discovery was not immediately announced, as the decay energy of 294Og corresponded to 212mPo.
In 2005, Researchers produced more Oganesson atoms for the experiment confirmation.
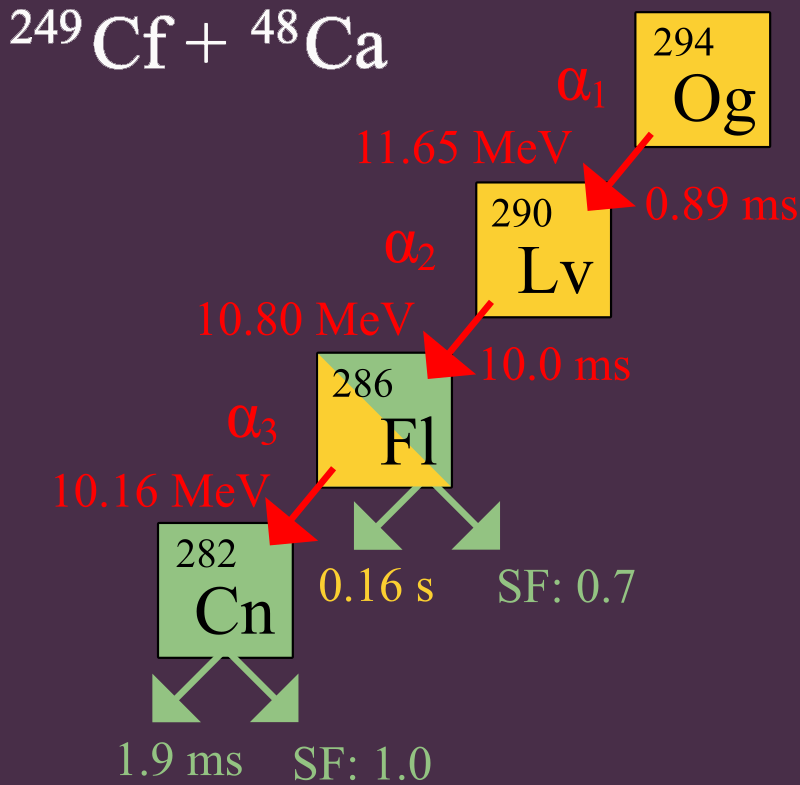
In 2006, th researchers announced that they had detected indirectly three or four nuclei of Oganesson-294 (1 or 2 in 2002 and 2 more nuclei in 2005), via collisions of Calcium-48 ions and Californium-249 atoms.
24998Cf + 4820Ca → 294118Og + 3 n.
In 2011, International union of pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) evaluated the results of 2006 of (JINR)-(LLNL) Collaboration.
In experiments, alpha-decay of three atoms of Ogenson was observed. A fourth decay was also proposed by direct spontaneous fission.
294118Og → 290116Lv + 42He
Identification of the 294Og nuclei was verified by separately creating 290Lv through a bombardment of 245Cm with 48Ca ions.
24596Cm + 4820Ca → 290116Lv + 3 n.
In June 2016, Discoverers planned to give the name of this Unknown discover element is Oganesson (Og) in honour of Yuri Ognesian, and finally on 29 Nov. 2016, the name became official.
Oganesson Uses
Since only a few atoms of Ogenson have ever been created, so at present, it has no practical use outside of the scientific study.
Biological role of Oganesson Element
It has no known biological role.
Sources of Oganesson
Russian scientists produced Oganesson through bombarded Californium’s atoms with calcium ions for 1,080 hours, got three atoms of Oganesson in resulted.
Oganesson Element Database
Atomic Spectroscopic Data
→ ASD Line
→ ASD Levels
→ Ground States and Ionization Energies
→ Handbook of Basic ASD
→ Energy Levels of Hydrogen and Deuterium
Atomic and Molecular Data
→ Electron-Impact Cross Sections
Bibliographic Databases on Atomic Spectroscopy
→ Atomic Transition Probability Bibliographic Database
→ Atomic Spectral Line Broadening Bibliographic Database
→ Atomic Energy Levels and Spectra Bibliographic Database
X-Ray and Gamma Ray Data
→ X-ray Attenuation and Absorption for Materials of Dosimetric Interest
→ XCOM: Photon Cross Section Database
→ Form Factor, Attenuation, and Scattering Tabulation
Radiation Dosimetry Data
→ Electrons (ESTAR)
→ Helium Ions (ASTAR)
→ Protons (PSTAR)
Nuclear Physics Data
→ Radionuclide Half-Life Measurements Data
→ Isotopic Compositions
Condensed Matter Physics Data
→ Atomic Reference Data for Electronic Structure Calculations
References
Wikipedia
National Institute of Standards and Technology
#Oganesson