12 Mg (Magnesium)
AMagnesium is a very light, shiny silvery-white, and fairly tough metal.
The element is very chemically active, where it takes place of hydrogen in boiling water and a huge amount of metals can be produced by thermic reduction of its salts and oxidized forms with magnesium.
It tarnishes slightly in air, and if magnesium divided finely, than it readily ignites upon heating in air, which burns with a dazzling (very bright) white flame.
It reacts readily with most non-metals and almost every acid.
Magnesium reacts slightly or not at all with most of the alkalis and many organic substances, like hydrocarbons, alcohols, amines, aldehides, phenols, esters and most of the oils.
Used as a catalyst, magnesium promotes organic reactions of Addition, Condensation, Dehalogenization, and Reduction.

Identity
CAS Number: CAS7439-95-4
CID Number: CID5462224
DOT Hazard Class: 4.1
DOT Number: 2950
CONTENT INDEX
Basic Properties of Magnesium
Pronunciation: mag-nee-zee-am
Appearance: Shiny grey solid
Mass Number: 24
Standard Atomic weight: 24.304, 24.307 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 12
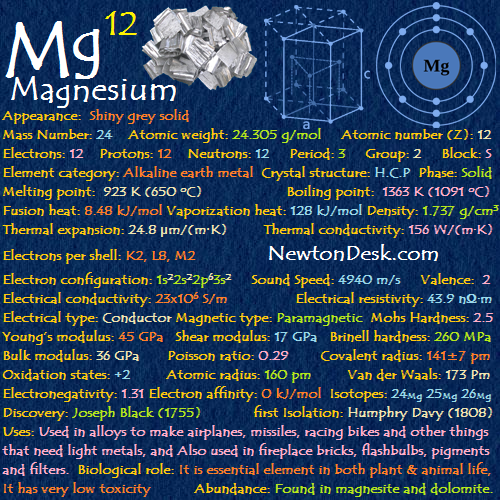
Electrons: 12
Protons: 12
Neutrons: 12
Period: 3
Group: 2
Block: s
Element category: Alkaline earth metal
Electrons per shell: K2, L8, M2
Electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s2
Thermal Properties of Magnesium
Phase: Solid
Melting point: 923 K (650 oC, 1202 oF)
Boiling point: 1363 K (1091 oC, 1994 oF)
Debye temperature: 318 K (44.85 oC, 112.73 oF)
Fusion heat: 8.48 kJ/mol
Vaporization heat: 128 kJ/mol
Specific heat: 1020 J/(kg K)
Molar heat capacity: 24.869 J/(mol.K)
Thermal expansion: 24.8 μm/(m∙K)
Thermal conductivity: 156 W/(m∙K)
Electrical properties of Magnesium
Electrical conductivity: 23×106 S/m
A Electrical resistivity: 43.9 nΩ∙m
A Electrical type: Conductor
Magnetic Properties of Magnesium
A Magnetic type: Paramagnetic
Magnetic susceptibility (xmol): +13.1×10-6 cm3/mol
Volume magnetic susceptibility: 0.000012
Mass magnetic susceptibility: 6.9×10-9 m3/kg
Molar magnetic susceptibility: 0.168×10-9 m3/mol
Physical Properties of Magnesium
Density: 1.737 g/cm3 (In solid) 1.585 g/cm3 (In Liquid at M.P)
Molar volume: 0.000013984 m3/mol
Young’s modulus: 45 GPa
Shear modulus: 17 GPa
Mohs Hardness: 1-2.5
Bulk modulus: 36 GPa
Poisson ratio: 0.29
Brinell hardness: 44-260 MPa
Sound Speed: 4940 m/s
Atomic Properties of Magnesium
Oxidation states: +2, +1
Valence Electrons: 3s2
Ion charge: Mg2+
The ionization potential of an atom: 7.61
Ionization energies: 1st: 737.6 kJ.mol 2nd: 1450.6 kJ/mol 3rd: 7732.6 kJ/mol
Ionic radius: 72 pm
Atomic radius: 160 pm (empirical)
Van der Waals: 173 Pm
Covalent radius: 141±7 pm
Filling Orbital: 3s2
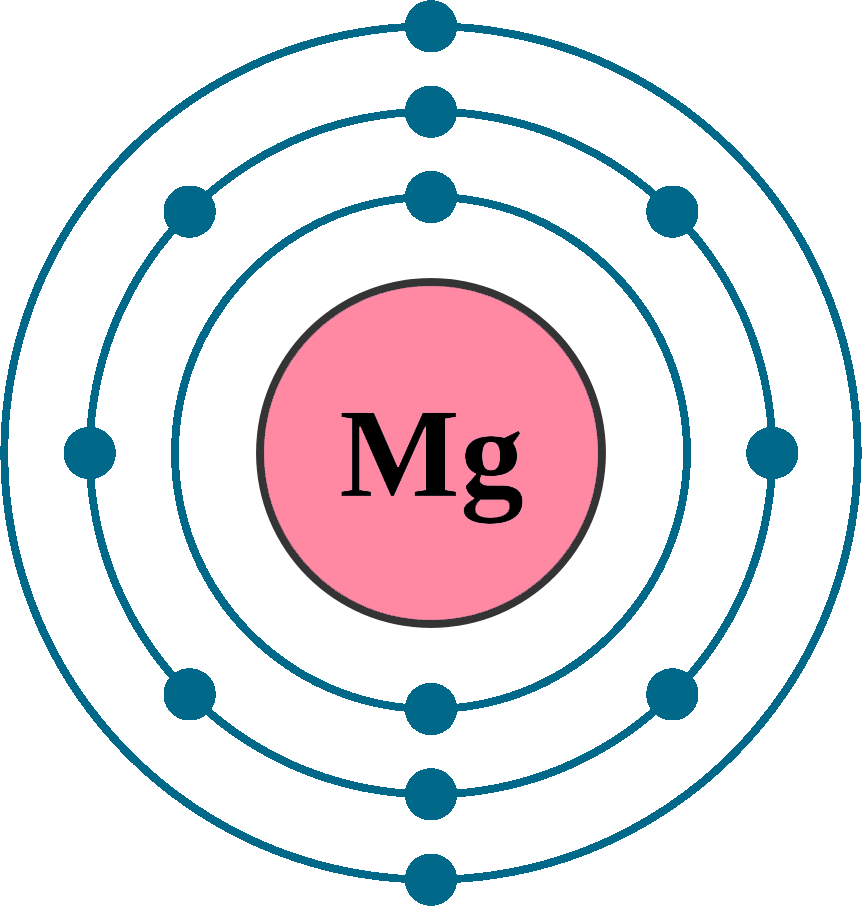
Crystal structure: Hexagonal close packed
Lattice angles: π/2, π/2, 2π/3
Lattice constant: 320.94, 320.94, 521.08 pm
Grid parameters: a=0.32094 Å c=0.52 Å
Attitude c/a: 1.624
Space Group Name: P63/mmc
Space Group Number: 194
Reactivity of Magnesium
Electronegativity: 1.31 (pauling scale)
Valence: 2
Electron affinity: 0 kJ/mol
Nuclear Properties of Magnesium
Half Life: Stable (Infinity)
Lifetime: Stable (Infinity)
Quantum Number: 1S0
Neutron cross section (Brans): 0.063
Neutron Mass Absorption: 0.0001
Isotopes: 24Mg 25Mg 26Mg
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Atomic Mass g/mol | Half Life (t1/2) |
| 24Mg | 79 | 23.984 | Stable |
| 25Mg | 10 | 24.985 | Stable |
| 26Mg | 11 | 25.982 | Stable |
Chemical Reactions of Magnesium
The metal reacts with oxygen at room temperature, and forming a passivating layer of MgO, and when Mg ignited, then it reacts with both oxygen & nitrogen forming a mixture of magnesium oxide & Magnesium nitride (Mg3N2):
2 Mg(s) + O2 (g) → 2 MgO (s)
3 Mg (s) + N2 (g) → Mg3N2 (s)
Mg does not react with liquid water at room temperature, but It reacts steam, and forming magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2), with excess steam & hydrogen gas:
Mg (s) + H2O (g) → MgO (aq) + H2 (g)
Mg (s) + 2 H2O (g) → Mg(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Metal Reacts with Cl2, and forming magnesium chloride:
Mg (s) + Cl2 (g) → MgCl2 (s)
The metal dissolves readily in acids, and forming Mg (II) ions & Hydrogen:
Mg (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → Mg2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) + H2 (g)
Mg (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → Mg2+ (aq) + 2 Cl– (aq) + H2 (g)
Mg (II) is precipitated by hydroxide ions (OH-), and Ammonia (NH3) will also precipitate Mg (II) as hydroxide, but the precipitation is incomplete:
Mg2+ (aq) + 2 OH– (aq) → Mg(OH)2 (s)
Production
To extract the Mg, firstly, calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) is added to seawater to form magnesium hydroxide precipitate:
MgCl2 + Ca(OH)2 → Mg(OH)2 + CaCl2
Brucite (Magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2) is insoluble in water, can be filtered out and reacted with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to produced concentrated magnesium chloride (MgCl2):
Mg(OH)2 + 2 HCl → MgCl2 + 2 H2O
Finaly, magnesium produces by electrolysis of magnesium chloride (MgCl2).
Magnesium History
Naming: After magnesia, in Greece
Discovery: Joseph Black (1755)
First Isolation: Humphry Davy (1808)
Magnesium Uses
Magnesium is 1/3rd less dense than aluminium.
It is used as alloying agent with aluminium to improve mechanical, fabrication and welding characteristics, these alloys are useful in car, missile, and aeroplane construction.
Magnesium is used in products for benefit of being lightweight, such as Laptops, Luggage, Car seats, Cameras, and Power tools, It is also added in molten iron & steel to remove sulfur.
It is used in producing nodular graphite cast iron, and as an additive to conventional propellants.
It is also used as a reducing agent (compound or element that loses an electron) in the production of pure uranium and other metals from their salts.
Magnesium ignites easily in air and burns with a very bright light, that’s why it’s used in flashlight Photography, Pyrotechnics, Fireworks, Flares, Sparklers, and Incendiary Bombs.

Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) is sometimes used as a mordant (dye fixative) for dyes.
Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) is added to plastics to make them fire retardant ( to slow or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity).
Dead-burned magnesite (Magnesium oxide, MgO) is used as refractory material to make Heat-resistant bricks for fire places, Furnaces, & Convertors.
It is a mineral supplement which is used to treat or prevent low level of Magnesium, that’s why it is also added in cattle feed & fertilisers.
Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia, Mg(OH)2), magnesium sulfate (Epsom salts, MgSO4), magnesium chloride (MgCl2), and magnesium citrate (C6H6MgO7) are all used in medicine.
Grignard reagents (RMgX, where R: alkyl or aryl and X: Halogens) are organic magnesium compounds that are important for the chemical industry.
It was used for a long time for synthesizing special & complex organic components.
Biological role of Magnesium
Organic Magnesium is very essential element in both plant & animal life.
Chlorophyll (magnesium-centred porphyrin complex, C20H14MgN4) is the chemical that allows plants to capture sunlight, and photosynthesis take place.
Without magnesium, photosynthesis could not take place, result to this plants would not grow, and animals life also would be finished.
Magnesium is essential for humans to the working of hundreds of enzymes (protein molecules in cells).
It is affected various factors like Weight, size etc..
Humans daily intake (Adult) around 240–370 mg (milligrams) of magnesium, and stores around 20 grams in our bodies, mainly in the bones to preventing osteoporosis.
It is also benefits in Diabetes, Heart health, Premenstrual syndrome, Migraine headaches, Healthy bones, Relieving anxiety etc..
It has very low toxicity, and not considered to be hazardous to health, but Inhalation dust may irritate mucous membranes or upper respiratory tract like eyes, skin etc..
Magnesium dust explosion possible if in granular or powder form, mixed with air.
It should be handle with great care, because the substance may spontaneously ignite on contact with air, where it can occur serious fires, especially when finely divided.
Once it catch fire, you can’t extinguish it by water (H2O), CO2, soil (SiO2) and other oxygen compounds, Because burning magnesium catches oxygen atoms and start to burning again.
For extinguish magnesium fire, oxygen supply should be cut off.
|
Magnesium Rich Foods |
||
| Food | Quantity | Contain Magnesium |
| Dark Chocolate | 28 grams (1 ounce) | 64 Mg |
| Avocados | 1 medium avocado | 58 mg |
| Cashews (Nuts) | 28 grams (1 ounce) | 80 mg |
| Almonds (Nuts) | 28 grams (1 ounce) | 85 mg |
| Peanut Butter | 2 tablespoons | 50 mg |
| Cooked Black Beans (Legumes ) | 170 grams (1 Cup) | 120 mg |
| Soymilk | 1 Cup | 61 mg |
| Cow’s milk | 1 Cup | 34 mg |
| Tofu (Staple food) | 100 grams (3.5 ounce) | 53 mg |
| Pumpkin Seeds | 28 grams (1 ounce) | 150 mg |
| Dry Roasted Sunflower Seeds | 1 Cup | 512 mg |
| Roasted Sesame Seeds | 28 grams (1 ounce) | 101 mg |
| Dry Buck Wheat (Whole Grains) | 28 grams (1 ounce) | 65 mg |
| Bread (Whole Wheat) | 1 Slice | 23 mg |
| Cooked Oatmeal | 1 Cup | 58 mg |
| Salmon packs (Fatty Fish) | 178 grams (6.4 ounce) | 53 mg |
| Bananas | 1 Large Banana | 37 mg |
| Cooked Spinach (Leafy Greens) | 180 grams (1 Cup) | 157 mg |
| Cooked Broccoli | 1 Cup | 51 mg |
| Cooked Shelled Edamame | 1 Cup | 100 mg |
Abundance of Magnesium
AMagnesium is the 8th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust,and the 3rd most abundance element dissolved in seawater, but it doesn’t found free in nature.
It is found in more than 60 minerals, but Magnesite, Dolomite, Carnallite, forsterite, Talc, and Olovine are of commercial importance, however, the mangnesium is largely deposits in magnesite and dolomite.
The sea contains Trillions of tones (0.13%) of magnesium, and each year produced 15,50,000 tonnes from this source.
It is prepared by reducing magnesium oxide (MgO) with silicon (Si), or by the electrolysis (chemical decomposition by electric current) of fused magnesium chloride (MgCl2) derived from wells, brines, & sea water..


Annual world wide production is around 18,000,000 tonnes
0.059% (In Universe)
12% (In Meteorites)
0.07% (In Sun)
2.9% (In Earth’s Crust)
0.13% (In Oceans)
0.027% (In Humans)
World’s Top producers of Magnesium
1) South Africa
2) China
3) Australia
4) Gabon
5) Brazil
World’s Top 3 Reserve holders of Magnesium
1) Russia
2) China
3) North Korea
Magnesium Price
Pure (99.99%) metal price is around $68-$70 per KG (KiloGram)
#magnesium


