Classification of Elements In Periodic Table (Block, Periods, Groups, and Categories)
CONTENT INDEX
About Elements In Periodic Table:
- These are the purest form of any known substance.
- They are composed of only the same type of atoms.
- There are neither proportions nor random mixing of substances so, we can say that mixtures are made up of elements.
- In nature, elements are the basic forms of every material that we found around, and hence order to study every substance around us, we need to begin with studying various elements.
- Do you know the number of elements astonishingly that number of elements that we find naturally occurring is 98, while the total number of elements known to mankind is 118?
- So, how do we study each element individually for all its properties? It is very difficult to pick every element individually and study all the properties. So, arranging the various elements is the first step towards understanding their properties. And the arrangement is possible only if we categorize them. This is how we organize the elements and this process of categorization helps study the elements with ease.
- In other words, we have classified the elements here.
- Classification of elements is categorizing the various elements into groups based on similarities and differences in their properties.
- The classification systems help us in grouping the various elements into categories, which we refer to as periods hence the system is also referred to as the periodic classification of elements.
Classification of elements
Grouping or sorting of elements based on their similarities and differences. It makes their study much easier.
Dobereiner’s traids 1829:
- Approximately less than 33 elements were known during that time.
- When elements are placed in increasing order of their atomic mass in group of three(triads) then the arithmetic mean of mass of 1st and 3rd element is found approximate equal to mass of central atom.
- Example; Li, Na, K- 7, 23,39.
Limitations; Dobereiner could find only three triads. That is total of 9 elements only. It is applicable only 9 elements.
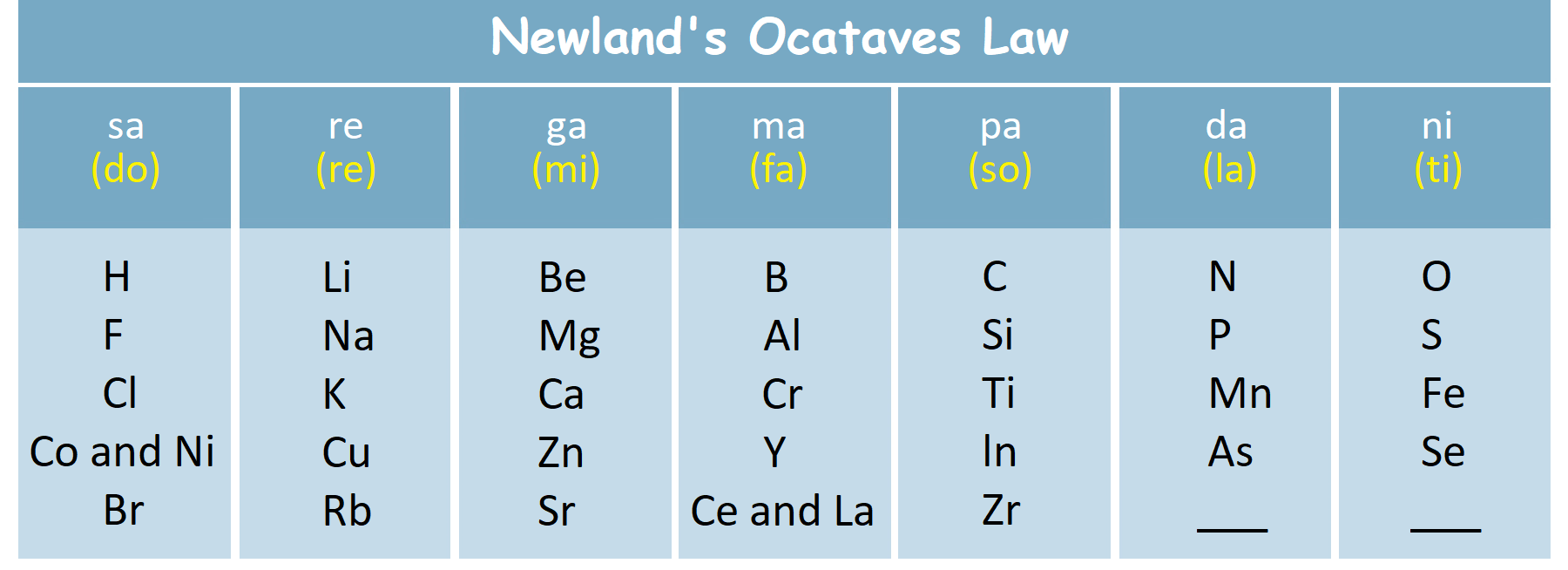
Newland’s law of octaves: till then 56 elements were known that time. The attribute of every eighth element (beginning with the first element) repeats if elements are grouped in increasing order of their atomic masses
Limitations– Only calcium showed similarity in qualities according to the law. He stated that only 56 elements existed in nature. Dissimilar elements were placed in same slot. While similar elements were placed in different slot.
Mendeleev’s periodic table (1869): 63 elements were known that time. The properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses.
Elements are Classified Basically Into Three Categories
1) Metals
2) Metalloids
3) Non- metals
- About 70% percent of the elements are metals, while the remaining 30% are nonmetals.
- Metallic elements share some similar properties while nonmetallic elements have their own set of properties.
- There is total 118 elements.
Atomic number: The number of protons contained in the nucleus of every atom of that element is known as its atomic number.
Henry Moseley, an English physicist, established in 1913 A.D. that an element’s atomic number(z) is a more fundamental attribute of an element than its atomic mass.
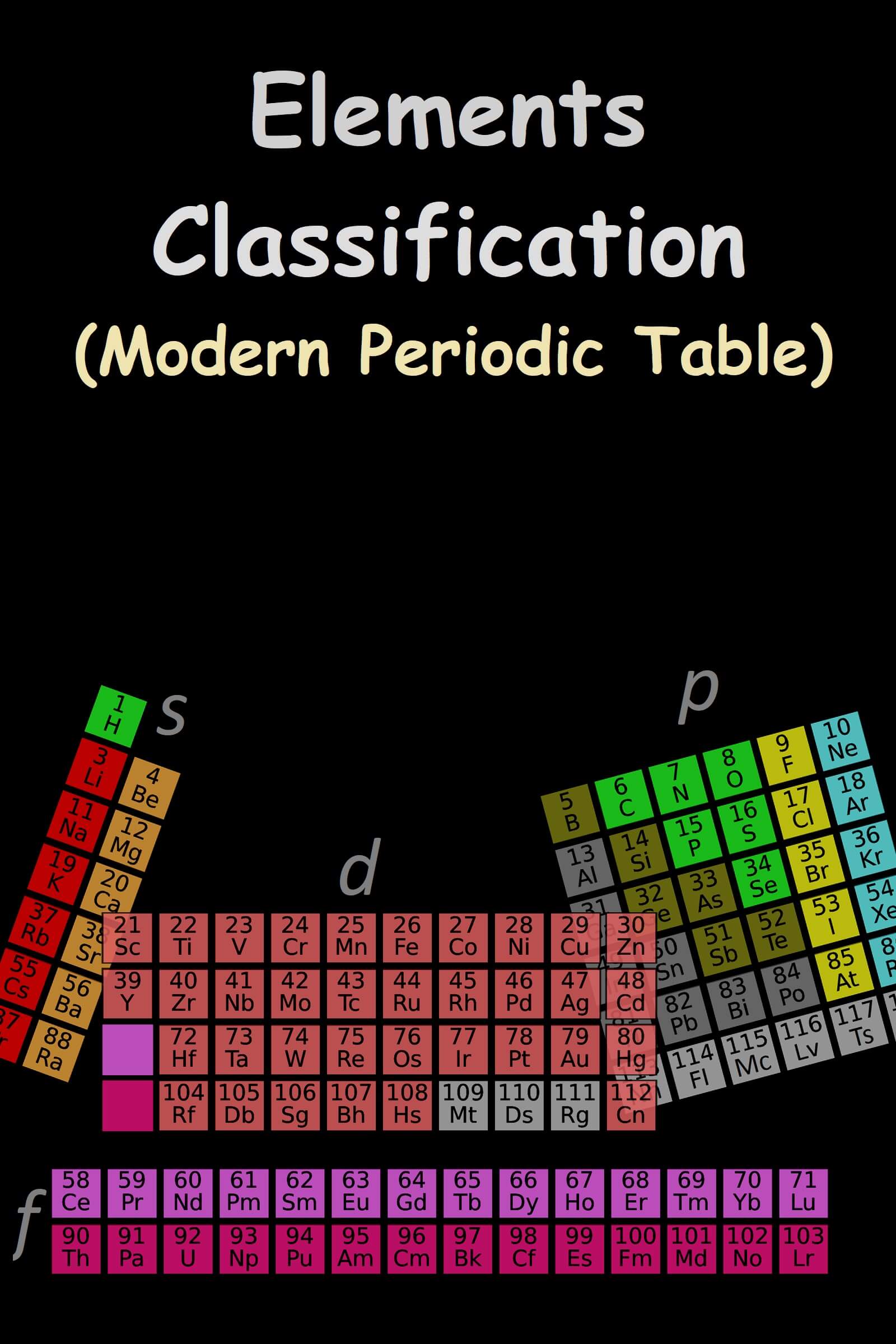
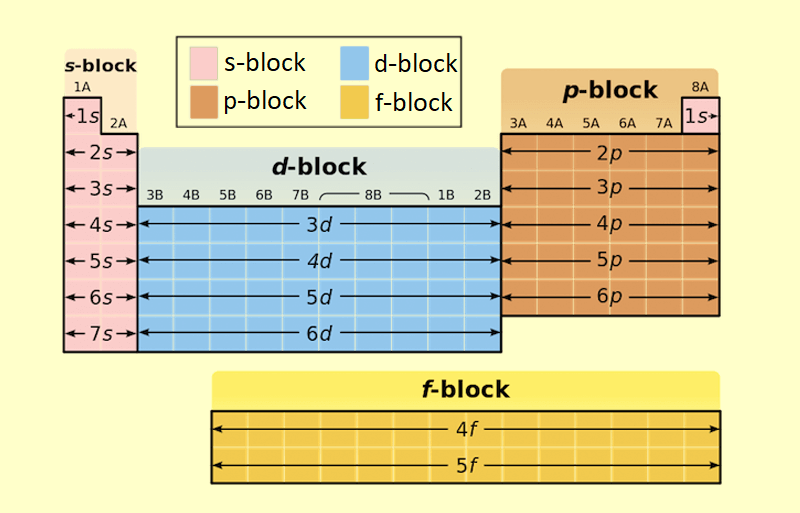
Modern periodic law: The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers, according to modern periodic law. It is divided into four blocks;
1) s block
2) p block
3) d block
4) f block
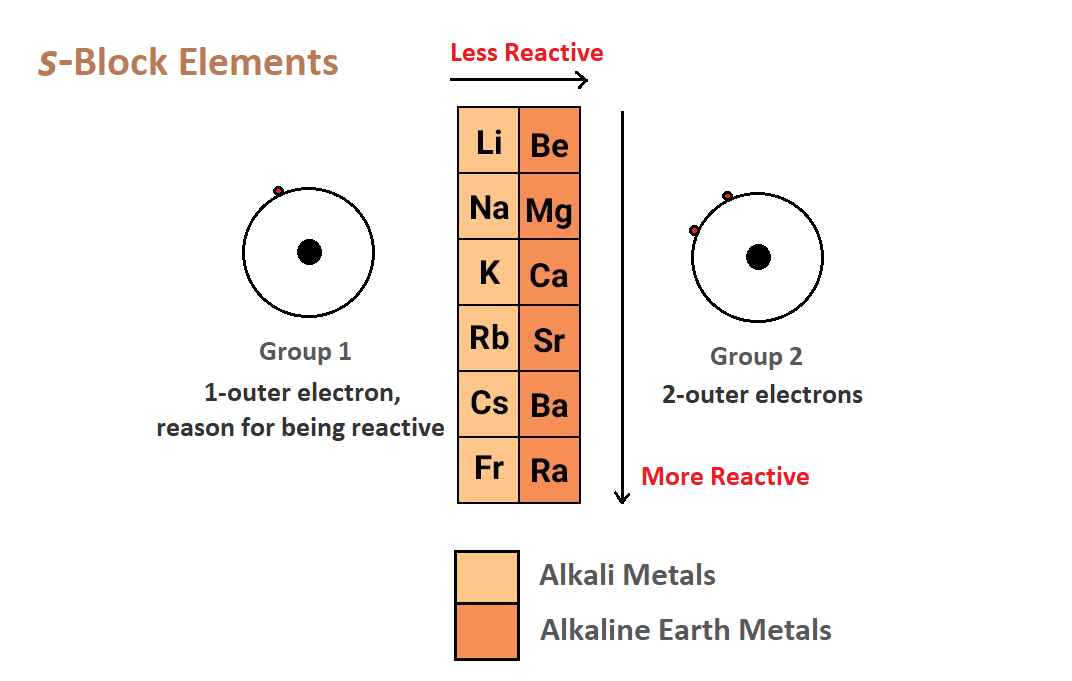
S Block Elements:
- If last electron of element enter in s subshell or orbital called s block element.
- 1st or 2nd group are comes in s block.
- 1st group are of alkali metals while 2nd group are of alkaline earth metals.
General properties of alkali metals
- Except hydrogen all other are metals.
- Metallic bond strength moving down the group decreases.
- Electronic configuration is ns1
- Melting point decreases when we go down the group.
- Ductile nature decreases when we moving down the group.
- When we go down the group electropositive nature of elements are increases.
- Reactivity of metals are decreases when we moving down the group.
- Volume and mass of the metals are increases when moving down the group.
- All metals are soft metal and good conductor of heat and electricity.
- Metals are highly reactive with water.
- Their ionization potential is very low due to formation of inert gas configuration.
General properties of non metals
- These metals have electrons in their valence shell and aside from beryllium can lose this valence electrons to shape an ion with a +2 fee like the alkali metals.
- These metals besides for magnesium are stored in oil comparable properties and reactivity tendencies also are observed.
- Moving down the group their density and reactivity will increase.
- Melting points and boiling points decreases moving down the group.
- Moving down the group metallic bond strength decreases.
- Ionic character of metal salt moving down the group increases.
- S block elements show less ionization energy so they show color flame in flame test.
- Be and mg do not show flame test due to high value of ionization energy.
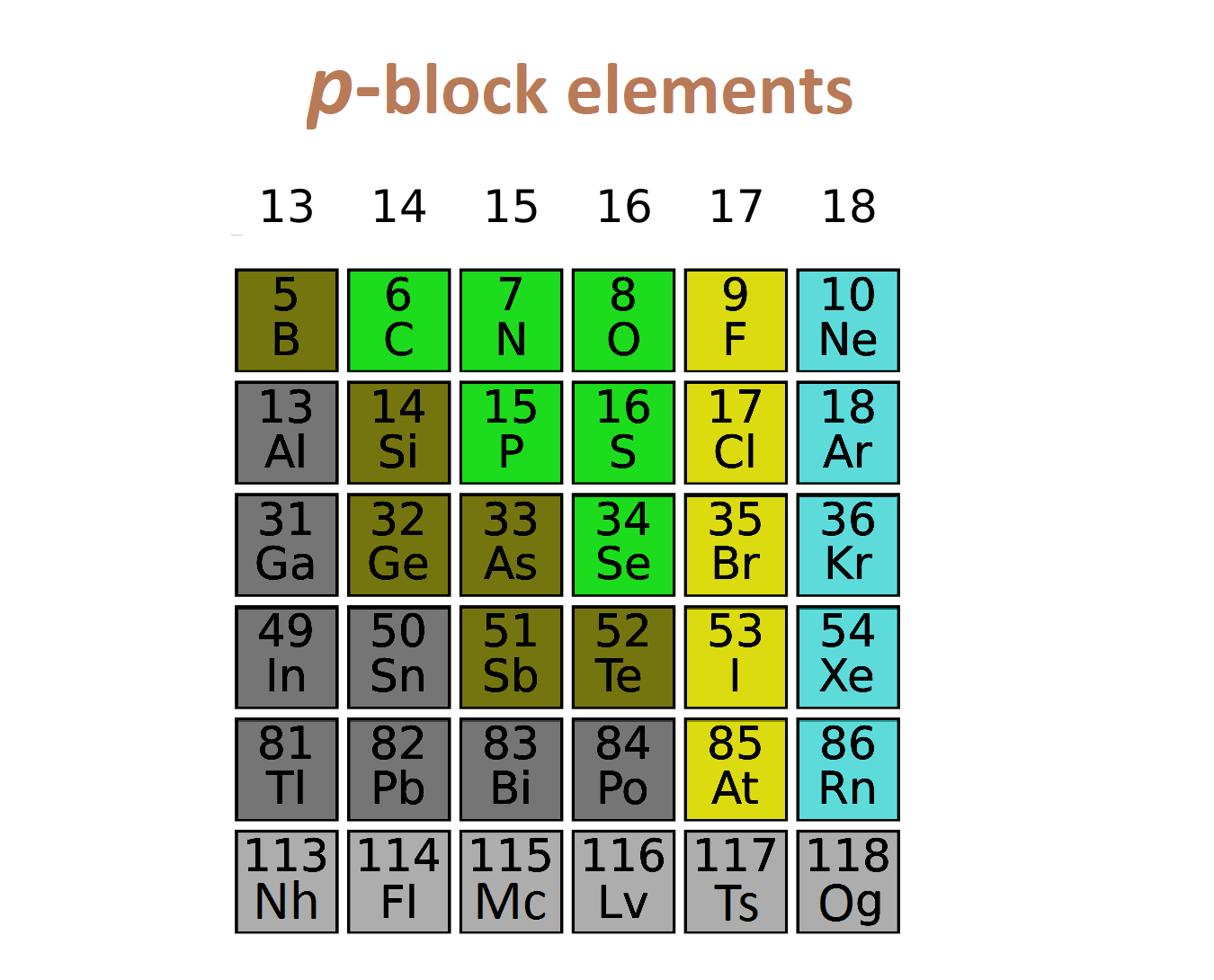
P Block Elements:
If last electron enter in p subshell then they are called p block elements.
- P block elements are metal , nonmetal or metalloid.
- P block elements are solid/liquid/gas.
- All inert gas except He are p block element.
- Generally they are bad conductor of heat and electricity.
- P block elements start from 13 and finished at 18th
- General electronic configuration ns2(n-2) f14(n-1) d10np1-6
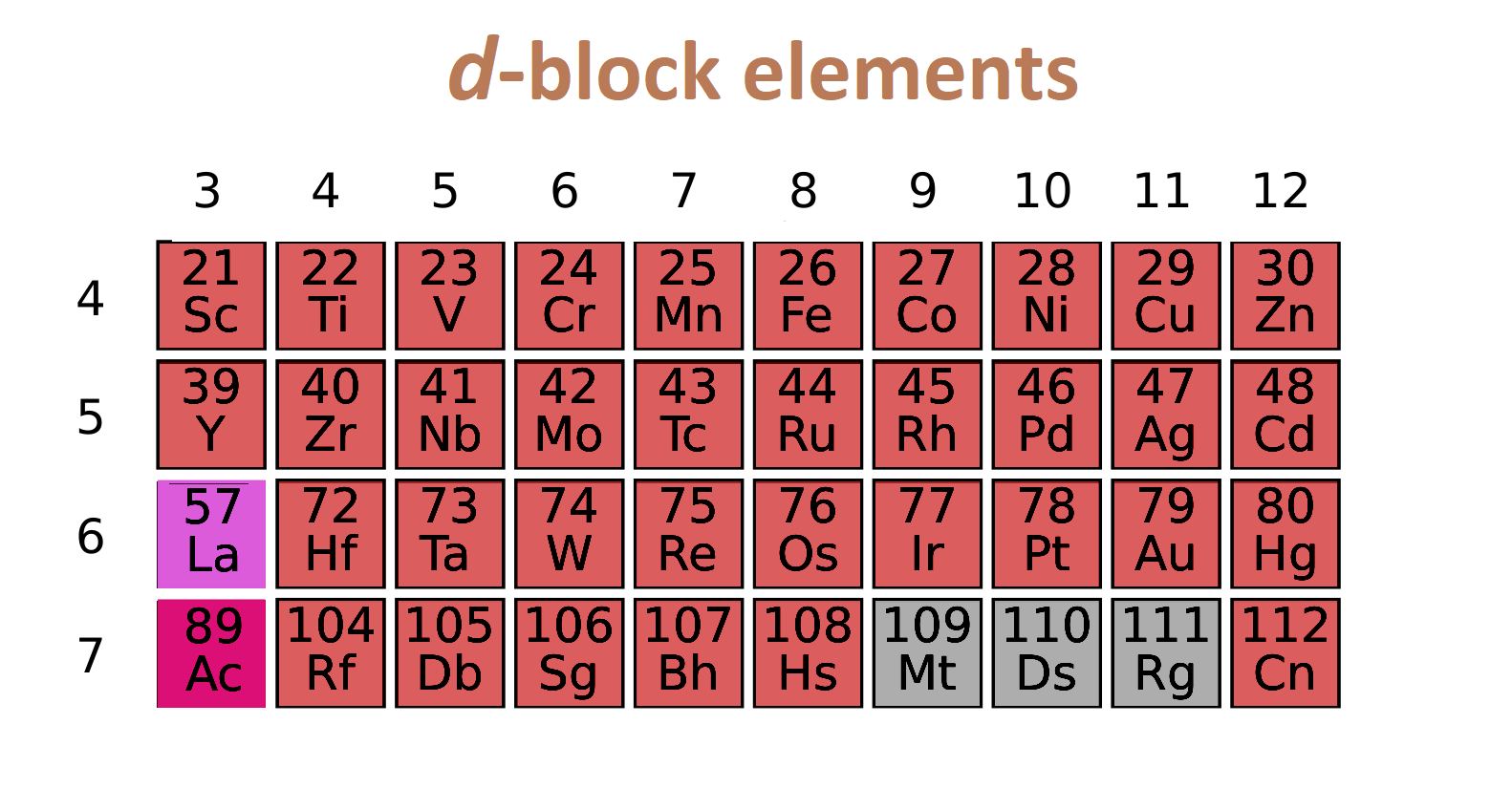
D block elements:
If last electron enter in d subshell then elements is called d block elements.
- If metal or stable metal ion have empty d subshell, then metal called transition element.(except Zn).
- Zn, Cd, Hg are d block element but not transition.
- Cu is transition element as well as d block element.
- Electronic configuration is (n-1)d1-10ns0-2
- All d block elements are solid (except Hg).
- All d block elements are good conductor of electricity and heat.
- Their melting point and boiling point is very high.
- They are good ductile.
- Density of d block metal is very high.
- Most dense element is osmium and iridium.
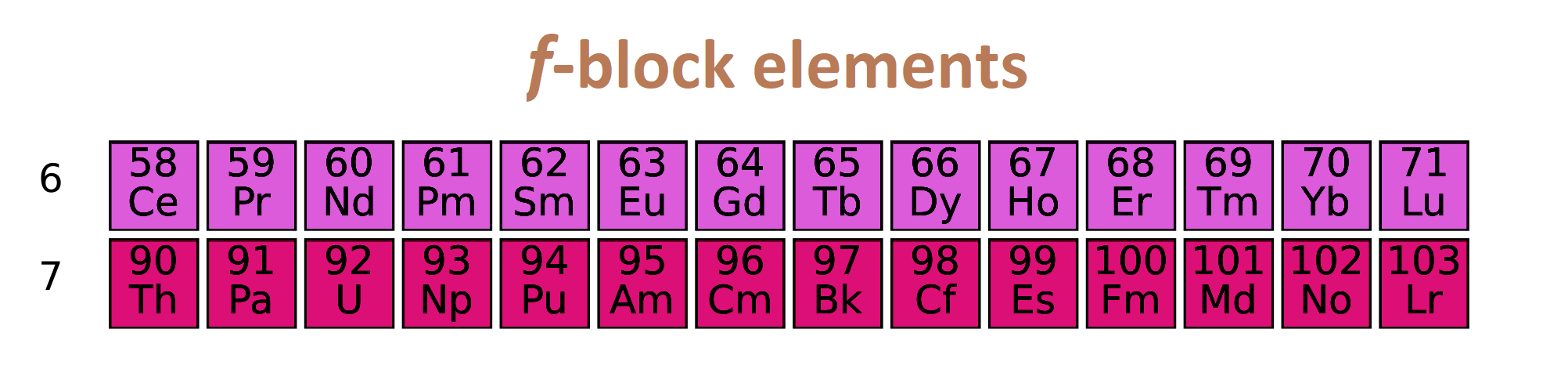
F block elements:
If last electron enter in f subshell, then element is called f block element.
- They are comes in group 3.
- Electronic configuration of f block element is (n-2)f1-14 (n-1)d0-1 ns2
- They are divided into two series lanthanoids and actinoids.
- They all are metals.
- They are generally hard.
- Their melting and boiling point is high.
- They are radioactive elements.
- They are good conductor of heat and electricity.
- They form two type of compound which is ionic or complex.
- They are colored in nature due to presence of unpaired electrons.
- Their oxidation state will be variable.