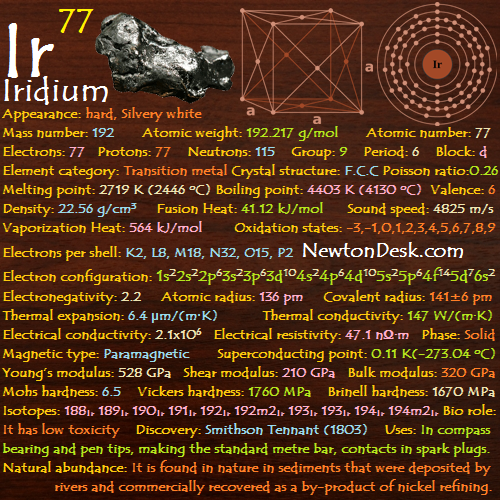
86 Rn (Radon)
Appearance: Colorless gas, Occasionally glows green or red in discharge tubes
Mass number: 222
Atomic weight: 222.0176 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 86
Electrons: 86
Protons: 86
Neutrons: 136
Group: 18
Period: 6
Block: P
Element category: Noble gas
Electrons per shell: K2, L8, M18, N32, O18, P8
Electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p64f145d106s26p6
Phase: Gas
Melting point: 202 K (-71 oC)
Boiling point: 211.5 K (-61 oC)
Density: 9.73 kg/m3 (in Gas), 4.4 g/cm3 (In Liquid at B.P)
Molar volume: 0.0228 m3/mol
Thermal conductivity: 0.00361 W/m*K)
Valence: 6
Electron affinity: 0 kJ/mol
Half Life(s): 330350
Lifetime(s): 476590
Decay mode: α decay
Neutron cross section (Barns): 0.7
Critical point: 377 K, 6.28 MPa
Heat of Fusion: 3.247 kJ/mol
Heat of vaporization: 18.10 kJ/mol
Molar heat capacity: 5R/2 = 20.786 J/(mol∙K)
Oxidation states: 2, 2, 0
Electronegativity: 2.2
Ionization energies: 1st: 1037 kJ/mol
Atomic radius: 120 pm
Covalent radius: 150 pm
Vander waals radius: 220 pm
Crystal structure: Face-centered cubic
Thermal conductivity: 3.61×10-3 W/(m∙K)
Magnetic ordering: non-magnetic
CAS Number: 10043-92-2
Discovery: Ernest Rutherford and Robert B. Owens (1899)
First isolation: William Ramsay and Robert Whytlaw-Gray (1910)
Isotopes: 210Rn 211Rn 222Rn 224Rn
Uses: useful in cancer therapy, treat tumours etc.. use in Home testing kits
Natural Abundance: Radon is produced naturally from the decay of the isotope radium-226, which is found in rocks
#radon