63 Eu (Europium)

Europium is a soft silvery metal, hard as lead and is quit ductile.
It is the most reactive metal, quickly oxidizing in air and seem like calcium in its reaction with water.
It Ignites quickly in air at about 150 oC to 180 oC.
With the development of ion-exchange techniques and special processes, the cost of the metal has been greatly reduced in recent years.

Identity
CAS Number: CAS7440-53-1
CID Number: CID23981
CONTENT INDEX
Basic Properties of Europium
Pronunciation: Yoor-oh-pee-am
Appearance: Silvery white, with a pale yellow tint (but it rarely seen without oxide discoloration)
Mass Number: 152
Standard Atomic weight: 151.964 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 63
Electrons: 63
Protons: 63
Neutrons: 89
Period: 6
Block: f
Element category: Lanthanide
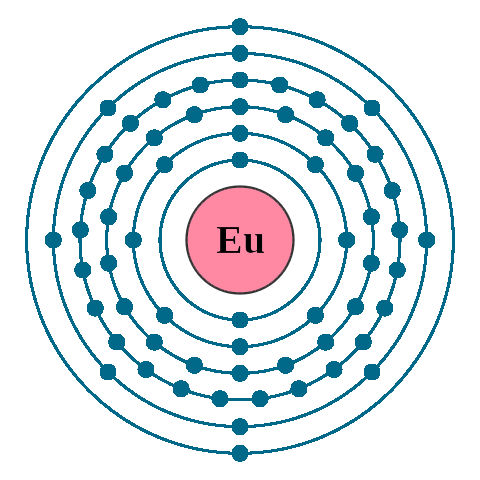
Electrons per shell: K2, L8, M18, N25, O8, P2
Electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p64f76s2
Thermal Properties of Europium
Phase: Solid
Melting point: 1099 K (826 oC, 1519 oF)
Boiling point: 1802 K (1529 oC, 2784 oF)
Fusion heat: 9.21 kJ/mol
Vaporization heat: 176 kJ/mol
Molar heat capacity: 27.66 J/(mol.K)
Thermal expansion: poly: 35.0 μm/(m∙K)
Thermal conductivity: est. 13.9 W/(m∙K)
Neel Point (magnetic ordering temperature) TN: 90.5 K (Temperature, above which an antiferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic)
Electrical properties of Europium
Electrical conductivity: 1.1×106 S/m
a Electrical resistivity: poly: 0.900 μΩ∙m
a Electrical type: Conductor
Critical point (Superconducting point): 1.8 K (value measured at 80 GPa)
Magnetic Properties of Europium
a Magnetic type: Paramagnetic
Magnetic susceptibility (xmol): +34,000×10-6 cm3/mol
Volume magnetic susceptibility: 0.0014473
Mass magnetic susceptibility: 276×10-9 m3/kg
Molar magnetic susceptibility: 41.942×10-9 m3/mol
Physical Properties of Europium
Density: 5.264 g/cm3 (In solid) 5.13 g/cm3 (In Liquid)
Molar volume: 0.00002898 m3/mol
Young’s modulus: 18.2 GPa
Shear modulus: 7.9 GPa
Bulk modulus: 8.3 GPa
Poisson ratio: 0.152
Mohs hardness: 3.7
Vicker hardness: 165-200 MPa
Sound Speed: 2680 m/s
Atomic Properties of Europium
Oxidation states: 3,2
Valence Electrons: 4f7 6s2
Ion charge: Eu3+ Eu2+
Ionization energies: 1st: 547.1 kJ.mol 2nd: 1085 kJ/mol 3rd: 2404 kJ/mol
Ionic radius: 94.7 pm
Atomic radius: 233 pm (Van der Waals)
Covalent radius: 198±6 pm
Filling Orbital: 4f7
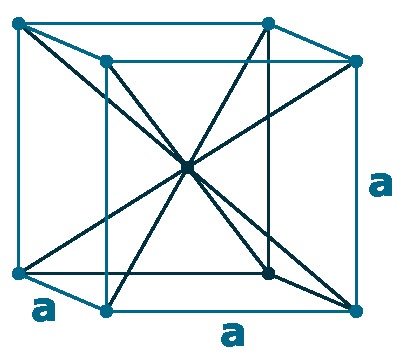
Crystal structure: Body-centered cubic
Lattice angles: π/2, π/2, π/2
Lattice constant: 458.1, 458.1, 458.1 pm
Grid parameters: 4.581 Å
Space Group Name: lm_3m
Space Group Number: 229
Reactivity of Europium
Electronegativity: pauling scale: 1.2
Valence: +3
Electron affinity: 50 kJ/mol
Nuclear Properties of Europium
Half Life: Stable (Infinity)
Lifetime: Stable (Infinity)
Quantum Number: 8S7/2
Neutron cross section (Brans): 4450
Neutron Mass Absorption: 0.6
Isotopes: 150Eu 151Eu 152Eu 153Eu 154Eu 155Eu
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Atomic Mass g/mol | Half Life (t1/2) |
| 150Eu | Syn | – | 36.9 y |
| 151Eu | 47.8 | 150.920 | 5×1018 y |
| 152Eu | Syn | – | 13.54 y |
| 153Eu | 52.2 | 152.921 | Stable |
| 154Eu | Eyn | – | 8.59 y |
| 155Eu | Syn | – | 4.76 y |
Chemical Reactions
Europium burns readily at 150 oC to form Europium (lll) oxide:
4 Eu + 3 O2 → 2 Eu2O3
Reacts with water:
2 Eu (s) + 6 H2O (g) → 2 Eu(OH)3 (aq) + 3 H2 (g)
The metal reacts with all Halogens to form Europium (lll) halides:
2 Eu (s) + 3 F2 (g) → 2 EuF3 (s) [white] (Europium (lll) fluoride)
2 Eu (s) + 3 Cl2 (g) → 2 EuCl3 (s) [yellow] (Europium (lll) chloride)
2 Eu (s) + 3 Br2 (g) → 2 EuBr3 (s) [gray] (Europium (lll) bromide)
2 Eu (s) + 3 I2 (g) → 2 EuI3 (s) (Europium (lll) iodide)
Dissolves readily in dilute sulfuric acid to form hydrated Europium (lll) (pale pink solution):
2 Eu + 3 H2SO4 + 18 H2O → 2 [Eu(H2O)9]3+ + 3 SO42− + 3 H2
Europium History
Naming: After Europe
Discovery: Eugène-Anatole Demarçay(1896, 1901)
Europium Uses
Europium is excellent neutrons absorber, It used in control rods of nuclear reactors.
It glows red under UV light.
For Powerful street lighting, Low-energy light bulbs(mercury vapour lamps) contain a little europium to give a more natural light, by balancing the blue (cold) light with a little red (warm) light.
A Salt (oxide) of europiums is used for newer phosphorescent (Glow in the dark) powder and paints.
Europium-doped plastic has been used as a laser material.
Biological role: It is Low-toxic, But it should be handled with care.
Abundance of Europium
Europium is chiefly Found in the minerals monazite and bastnaesite.
It is Prepared by mixing Europium (III) oxide (Eu2O3) with a 10%-excess of lanthanum metal and heating the mixture under high vacuum in a tantalum crucible, and It’s collected as a silvery-white metallic deposit on the crucible wall.
Annual world wide production is around 400 tons.
5×10-8% (In Universe)
5.9×10-6% (In Meteorites)
5×10-8% (In Sun)
0.00018% (In Earth’s Crust)
1.3×10-11% (In Oceans)
World’s Top 3 producers of Europium
1) China
2) Russia
3) Malaysia
World’s Top 3 Reserve holders of Europium
1) China
2) CIS Countries (inc. Russia)
3) USA
#Europium



This is actually useful, thanks.