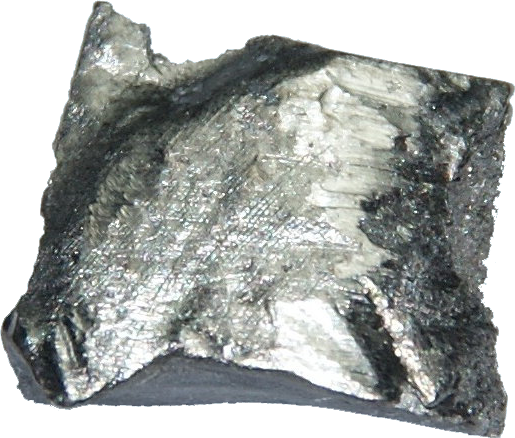
65 Tb (Terbium)

It is a soft, malleable, ductile, silver-gray metal.
It is stable in air, but it is slowly oxidised and it reacts with cold water.

Identity
CAS Number: CAS7440-27-9
CID Number: CID23958
CONTENT INDEX
Basic Properties of Terbium
Pronunciation: Tur-bee-am
Appearance: Silvery white
Mass Number: 158
Standard Atomic weight: 158.925 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 65
Electrons: 65
Protons: 65
Neutrons: 93
Period: 6
Block: f
Element category: Lanthanide
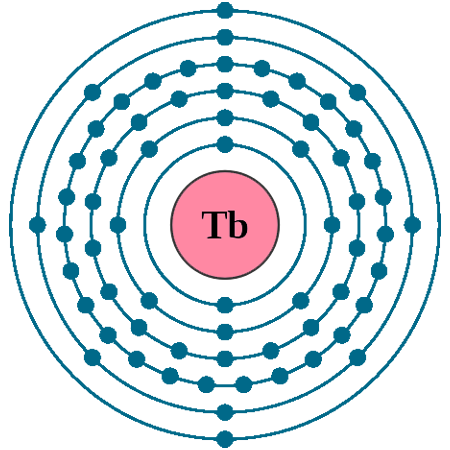
Electrons per shell: K2, L8, M18, N27, O8, P2
Electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p64f96s2
Thermal Properties of Terbium
Phase: Solid
Melting point: 1629 K (1356 oC, 2473 oF)
Boiling point: 3396 K (3123 oC, 5653 oF)
Fusion heat: 10.15 kJ/mol
Vaporization heat: 391 kJ/mol
Molar heat capacity: 28.91 J/(mol.K)
Thermal expansion: α, poly: 10.3 μm/(m∙K)
Thermal conductivity: 11.1 W/(m∙K)
Neel Point: 230 K
Electrical properties of Terbium
Electrical conductivity: 8.3×106 S/m
a Electrical resistivity: α, poly: 1.150 μΩ∙m
a Electrical type: Conductor
Magnetic Properties of Terbium
Magnetic type: Paramagnetic
Curie point: 222 K
Magnetic susceptibility (xmol): +146,000×10-6 cm3/mol
Volume magnetic susceptibility: 0.1117784
Mass magnetic susceptibility: 13600×10-9 m3/kg
Molar magnetic susceptibility: 2161.385×10-9 m3/mol
Physical Properties of Terbium
Density: 8.23 g/cm3 (In solid) 7.65 g/cm3 (In Liquid)
Molar volume: 0.00001934 m3/mol
Young’s modulus: α form: 55.7 GPa
Shear modulus: α form: 22.1 GPa
Mohs Hardness: 2.33
Bulk modulus: α form: 38.7 GPa
Poisson ratio: α form: 0.261
Vicker hardness: 450-865 MPa
Brinell hardness: 675-1200 MPa
Sound Speed: 2620 m/s
Atomic Properties of Terbium
Oxidation states: 4, 3, 2, 1
Valence Electrons: 4f9 6s2
Ion charge: Tb3+
Ionization energies: 1st: 565.8 kJ.mol 2nd: 1110 kJ/mol 3rd: 2114 kJ/mol
Ionic radius: 92.3 pm
Atomic radius: 221 pm (Van der Waals)
Covalent radius: 194±5 pm
Filling Orbital: 4f9
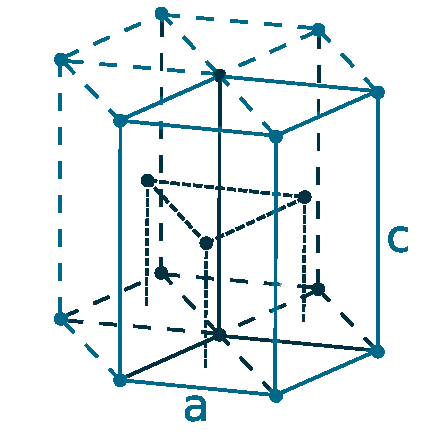
Crystal structure: Hexagonal close-packed
Lattice angles: π/2, π/2, π/3
Lattice constant: 360.0, 360.0, 569.39 pm
Grid parameters: a=3.600 Å, c=5.694 Å
Attitude c/a: 1.582
Space Group Name: P63/mmc
Space Group Number: 194
Reactivity of Terbium
Electronegativity: pauling scale: 1.2
Valence: +3
Electron affinity: 50 kJ/mol
Nuclear Properties of Terbium
Half Life: Stable (Infinity)
Lifetime: Stable (Infinity)
Quantum Number: 6H15/2
Neutron cross section (Brans): 23
Neutron Mass Absorption: 0.009
Isotopes: 157Tb 158Tb 159Tb
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Atomic Mass g/mol | Half Life (t1/2) |
| 157Tb | Syn | – | 71 y |
| 158Tb | Syn | – | 180 y |
| 159Tb | 100 | 158.925 | Stable |
Chemical Reactions
The metal oxidation slowly in air and burns readily to form a mixed terbium (lll,lV) oxide:
8 Tb + 7 O2 → 2 Tb4O7
Reacts slowly with cold water and quickly with hot water (form terbium hydroxide and hydrogen gas):
2 Tb + 6 H2O → 2 Tb(OH)3 + 3 H2↑
The metal reacts with all Halogens to form Terbium (lll) halides:
2 Tb (s) + 3 F2 (g) → 2 TbF3 (s) [white] (Terbium (lll) fluoride)
2 Tb (s) + 3 Cl2 (g) → 2 TbCl3 (s) [white] (Terbium (lll) chloride)
2 Tb (s) + 3 Br2 (g) → 2 TbBr3 (s) [white] (Terbium (lll) bromide)
2 Tb (s) + 3 I2 (g) → 2 TbI3 (s) (Terbium (lll) iodide)
Dissolves readily in dilute sulfuric acid to form Solutions containing Terbium (lll) ions (pale pink):
2 Tb (s) + 3 H2SO4(aq) → 2 Tb3+(aq) + 3 SO42−(aq) + 3 H2↑ (g)
Terbium History
Naming: From Ytterby (Sweden), Where it was mined
Discovery: Carl Gustaf Mosander (1843)
Terbium Uses
Terbium is expensive and rare element, so it has few commercial uses.
Some minor uses are in lasers, semiconductor devices, and phosphorous in colour television tubes.
Sodium terbium borate is used in solid-state devices.
ATerbium can be used with Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) as a crystal stabilizer of fuel cells which operate at high temperature.
It is also used in low-energy lightbulbs and mercury lamps.
It has been used to improve the safety of medical x-rays.
Terbium alloyed with dysprosium and iron lengthens and shortens in a magnetic field and has the highest magnetostriction of any alloy useful in magnetomechanical devices (Loudpeakers etc..)
Biological role: It is Low-toxic, But it should be handled with care.
Abundance of Terbium
Found in the minerals monazite and bastnaesite (chiefly in monazite ore).
It can be extracted by ion exchange and solvent extraction.
It is also obtained from euxenite, a complex oxide containing 1% or more of terbiums.
Terbium metal is produced commercially by reducing the anhydrous chloride or fluoride with calcium metal under a vacuum in a tantalum crucible.
It can also produce by the electrolysis of terbium-oxide in molten calcium chloride.
Annual world wide production is around 10 tons.
5×10-8% (In Universe)
3.9×10-6% (In Meteorites)
1×10-8% (In Sun)
0.000093% (In Earth’s Crust)
1.4×10-11% (In Oceans)
World’s Top 3 producers of Terbium
1) China
2) Russia
3) Malaysia
World’s Top 3 Reserve holders of Terbium
1) China
2) CIS Countries (inc. Russia)
3) USA
#terbium